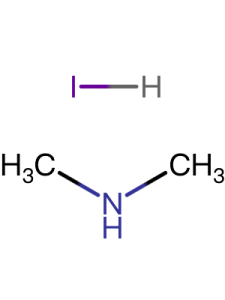
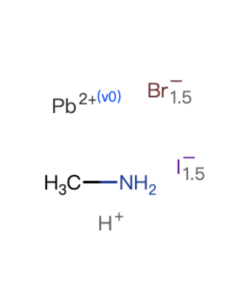
| Purity | 99.5% |
| CAS Number | 69276-12-6 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Linear Formula | CH6Cl3NPb |
| Mol. Weight | 345.62 |
| Stock Name | MAPbCl3 |
| Name(EN) | MAPbCl3 |
| Synonym | CH3NH3PbCl3/MAPbCl3 |
Crystal orientation-dependent optoelectronic properties of MAPbCl3 single crystals
Cheng, Xiaohua; Jing, Lin; Zhao, Ying; Du, Songjie; Ding, Jianxu; Zhou, Tianliang [Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, vol. 6, # 6, p. 1579 - 1586]
Abstract
Hybrid perovskite MAPbCl3 is considered to be one of the most promising candidates applied in visible-blind UV-photo-detectors due to its outstanding optoelectronic properties. It is proved that the MAPbCl3 single crystal is more excellent than its polycrystalline counterpart because of its fewer defects and grain boundaries. When referring to a single crystal, the crystal orientation or crystal structure anisotropy is an inevitable topic, because structure anisotropy can affect or decide the optoelectronic properties of single crystals. In this study, both cubic and triangular prism MAPbCl3 single crystals with (100) and (110) crystallographic planes were successfully grown from mixed solutions. The crystal growth process, crystal structure and optical absorption were investigated. Moreover, by fabricating metal-semiconductor-metal (MSM) photo-detectors using Au interdigital electrodes on both (100) and (110) planes, the optoelectronic anisotropy was explored by comparing photocurrents, responsivity, external quantum efficiency and detectivity. According to the crystal structure and calculated charge density, the optoelectronic anisotropy in the MAPbCl3 single crystal was revealed.
Properties of CH3NH3PbX3 (X = I, Br, Cl) powders as precursors for organic/inorganic solar cells
Dimesso; Dimamay; Hamburger; Jaegermann [Chemistry of Materials, 2014, vol. 26, # 23, p. 6762 - 6770]Abstract
CH3NH3PbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) perovskites were prepared by a self-organization processes using different precursor solutions. The XRD analysis indicates the formation, at room temperature, of a tetragonal structure (space group I4/mcm) for X = I, of a cubic structure (space group Pm3m) for X = Br, and of centro-symmetric cubic structure (space group Pm3m) for X = Cl, respectively. The structural analysis revealed the formation of CH3NH3Cl as secondary phase in the Cl-containing system. The morphological investigation revealed the formation of rhombo-hexagonal dodecahedra crystallite for X = I, Br, whereas cube-like aggregates were observed for X = Cl. The thermogravimetric analysis performed in air did not reveal any loss until 250 °C for X = I and 300 °C for X = Br, respectively, whereas the differential thermal analysis (DTA) detected two endothermic thermal events (at 336 and 409 °C) for X = I and one only (379 °C) for X = Br, respectively. The infrared spectra (IR) of the powders conformed to the 3-fold symmetry of the methylammonium ion which rotates around the C-N axis. Optical absorption measurements indicated that the CH3NH3PbX3 systems behave as direct-gap semiconductors with energy band gaps of 1.53 eV for X = I, 2.20 eV for X = Br, and 3.00 eV for X = Cl, respectively, at room temperature. The direct-gap semiconductivity for X = I and X = Br was confirmed by the photoluminescence emission measurements, whereas the compound for X = Cl is inactive. I-containing powders were dissolved in an organic solvent (dimethyl-formamide, DMF). The dispersion (100-300 μL) was dropped on glassy substrates on which thick films were obtained by spin-coating and thermal treatment at 120 °C for ca. 5 min. The preparation of the layers was performed in air at room temperature.
Systematic studies on chain lengths, halide species, and well thicknesses for lead halide layered perovskite thin films
Takeoka, Yuko; Asai, Keisuke; Rikukawa, Masahiro; Sanui, Kohei [Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2006, vol. 79, # 10, p. 1607 - 1613]Abstract
Two-dimensional layered perovskite compounds, (CnH 2n+1NH3)2(CH3NH3) m-1PbmX3m+1 (n = 2, 3, 4, 6, and 10; X = Cl, Br, and I; m = 1, 2, and 3) were systematically prepared. The influences of the barrier-size, halide species, and well thickness of the perovskite thin films on the quantum confinement structures were investigated. The layered perovskite films showed a strong and clear absorption peak due to excitons confined in inorganic quantum-wells. The exciton peak shifted to lower energy as the halide species was changed from Cl to Br and I. Furthermore, fine multilayer perovskite compound films were prepared by varying the spin-coating conditions.
| Characteristic 1 | Cl |
| Characteristic 2 | Pb |