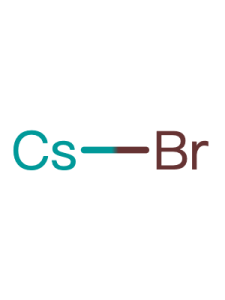| Notes |
XRD, user instruction for enquiring |
| Store |
25℃ under N2 atmosphere |
| Packaging |
25 g, or as required in glass bottle |
| Solubility |
High soluble in water and HI et al |
| Appearance |
White Powder |
| Purity |
99.99% |
| Linear Formula |
ICs |
| CAS Number |
7789-17-5
|
| Name(EN) |
CsI |
| Synonym |
CsI |
In recent years, carbon-based CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have attracted more attention due to their low cost and good stability. However, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of carbon-based CsPbI2Br PSCs is still no more than 16%, because of the defects in CsPbI2Br or at the interface with the electron transport layer (ETL), as well as the energy level mismatch, which lead to the loss of energy, thus limiting PCE values. Herein, a series of cadmium halides are introduced, including CdCl2, CdBr2 and CdI2 for dual direction thermal diffusion treatment. Some Cd2+ ions thermally diffuse downward to passivate the defects inside or on the surface of SnO2 ETL. Meanwhile, the energy level structure of SnO2 ETL is adjusted, which is in favor of the transfer of electron carriers and blocking holes. On the other hand, part of Cd2+ and Cl− ions thermally diffuse upward into the CsPbI2Br lattice to passivate crystal defects. Through dual direction thermal diffusion treatment by CdCl2, CdI2 and CdBr2, the performance of devices has been significantly improved, and their PCE has been increased from 13.01% of the original device to 14.47%, 14.31%, and 13.46%, respectively. According to existing reports, 14.47% is one of the highest PCE of carbon-based CsPbI2Br PSCs with SnO2 ETLs.